In our series of blogs on ‘How it works’ we are taking a closer look at the different aspects of using ultraviolet light for industrial curing purposes.
UV curing is a process that involves exposing resins, glue and ink to ultraviolet light to launch a chemical reaction which results in almost instantaneous drying or bonding. Using UV to cure substances has been adopted across many industries from printing to microchip processing board manufacturing. It is most probable that you are reading this blog whilst being in contact with a surface that has undergone UV curing as part of its production (the table, a pen, your laptop, a mobile phone etc.)
In this blog we look at the automotive industry and how over the past 20 years it has widely adopted UV curing as an integral part of the manufacturing process. The benefits to us all include faster production times and more durable components.
How UV curing happens
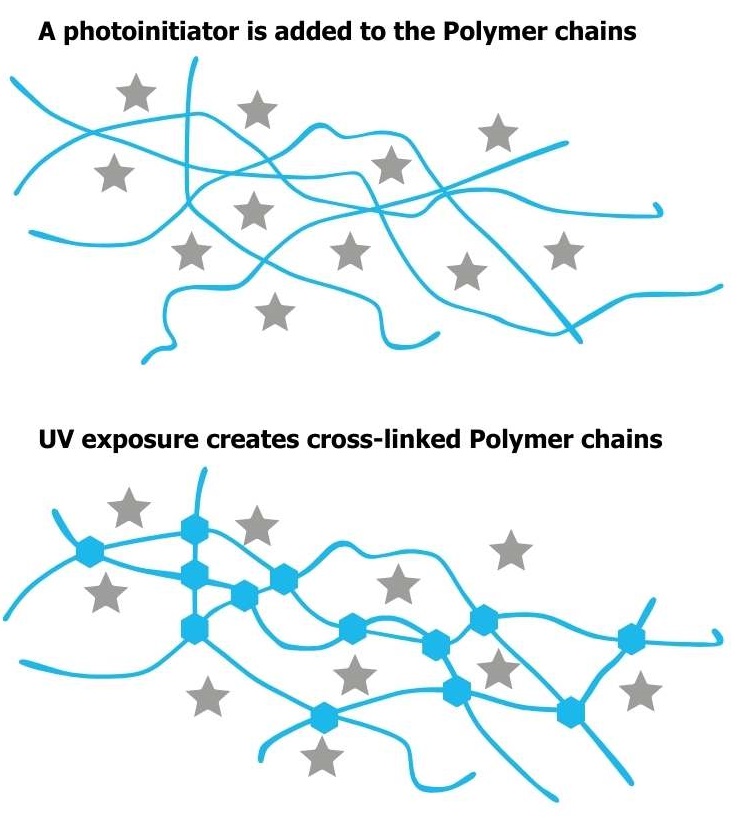
First, let’s take a quick look at how UV curing works and why it’s such a positive option to previous methods.
Historically curing methods adopted to help bond together, apply a coating or add a finish to products were based on triggering the evaporation process to elements. This required a lot of heat and took some time to achieve good results.
UV light does not use evaporation in its process to cure compounds but instead uses a process called polymerisation.
It works by adding a photoinitiator to the element that requires curing (resin, paint, ink, varnish etc). This does not alter the make-up of the element itself but when the photoinitiator is exposed to ultraviolet light polymerisation occurs which essentially means it almost instantly ‘drys’ or ‘glues’ to the substrate it is being applied to. The process is very fast and requires substantially less energy than previous methods.
How is UV curing used in the automotive industry?
For the automotive industry, there are many parts and components that require coating, gluing or finishes to be applied. The use of UV curing to do this has transformed the way vehicles are built.
Below is a list of the automotive production process that use UV curing. This is not necessarily exhaustive but does illustrate the range of uses the UV curing can be applied to.

Paint Booths
The application of body paint, both in the original production and in repair shops uses UV curing to dry paint in the fastest way possible. Substantially reducing the time needed to paint panels with both under and overcoats of paint.
Another relatively new use of UV curing at the paint stage is on clearcoats that are applied to the final finish on panels. Clearcoating was developed in the early 00’s as a way to improve durability and increase scratch resistance and was developed using UV as an integral part of the process.
Sheet Molding Compound( SMC) Body Panels
SMC is a composite material used as an alternative to steel in body panels. It’s easy and quicker to make and can be moulded into any shape required. The challenge with SMC is that it is semi-porous substance and so any painted finish on it can be prone to quality issues. To help reduce these problems UV curing is used to seal finishes, especially at the undercoat stage, thus improving the quality of the final finish.
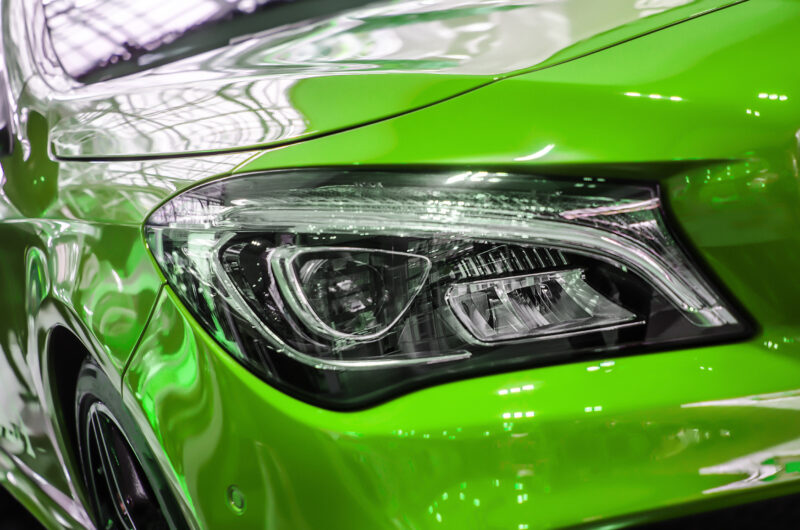

Headlamps
One of the most established uses of UV curing in the automotive industry is in producing headlamps. For over 15 years UV has been the standard technology used to apply finishes to make headlights more durable and effective.
The UV process is used to create very durable, hard-to-scratch headlight lens’ as well as creating ultra-smooth reflector surfaces. This creates improved protection from scratching, dust, and moisture. It also improves electrical conductivity and insulation.
Lithium-ion Batteries
With the increase in focus and production of electric vehicles, it is no surprise that UV curing is now being increasingly used in the production of lithium-ion batteries. It is a rapidly evolving solution in this field and can help improve battery performance and durability.
Component Production
A broad range of automotive interior and exterior components utilise UV curing to glue or add finishes. These include under the hood electronics, metal and plastic parts, brake discs and trims.
Liquid Gaskets
Gaskets are used to seal parts together or to ensure no leaks occur. In todays, modern automotive components gaskets can be sealed into place using UV cured liquids. This way of sealing means any shape, size or contour can be sealed effectively with a higher and more durable performance.
 Other parts
Other parts
UV curing has established itself as a stable and valuable way to add speed of production and durability to vehicle parts. The process is continuing to be developed for use across other parts of the manufacturing process including plastic coatings, interior finishes, alloy wheels and wheel covers.
Windscreen Repairs
Whilst not quite part of the production process, the use of UV curing is also widespread in the windscreen repair industry. The resin used to fix a crack or place the windscreen into its frame uses UV curing to quickly dry the compounds. The fact that the UV process doesn’t create any discolouration, means the repair remains clear in the drivers eyeline.
You can see from the above that ultraviolet light is a central and growing part of the automotive production process. Its speed, lower costs and versatility is making a huge difference in producing the vehicles we all use today and into the future.
If you’d like to know more about how Alpha-Cure’s UV lamps work within automotive curing systems, please Contact Us. Our sales team are here to help.
Latest Articles
Alpha-Cure Is Attending LabelExpo Southeast Asia – Meet Us
Alpha-Cure’s Commercial Director, Berenika Bond, will be attending LabelExpo Southeast Asia in Ban...
View ArticleNew Interactive UV Lamp Troubleshooting Tool Launched
Diagnose and Resolve Common Issues with Confidence Alpha-Cure has launched a brand-new interactive U...
View ArticleThe Benefits of Infrared Lamps and Where to Use Them
It’s been a while since we featured Infrared (IR) Lamps in our blog series, despite them being...
View ArticleOptimising UV Curing Processes in the Printing Industry: Techniques and Benefits
As we push into a new year, now a great time to review your current print curing system set ups and ...
View Article